1.3.4 Photoelectric cell sensor
Photoelectric cell sensors
Find all our ranges of photoelectric sensors:
- Female sensor connector leads
- Photoelectric sensor QD
- Compact sensor QB
- Fork sensor F5
- Cylindrical photoelectric sensor type DPIC
- Photoelectric sensor FA
- Cubic photoelectric sensor SQ
- Fixing brackets for sensors
- Reflector RL1
Photoelectric sensors
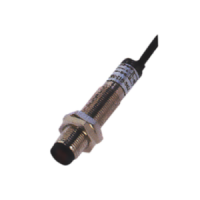
A photoelectric sensor includes a photosensor which changes depending on the intensity of a light radiation. It enables to detect the presence of an object or of an element thanks to a light beam.
Photoelectric sensors include a light emitter and receiver. If an object passes in front of the light beam of the industrial optical sensor, it will be sent back to the receiver.
They can be wired or with a M8 or M12 connector with a specific cable.
We also find several sizes: square, cylindrical or fork.
Photoelectric sensors can be used in the industrial sector, especially in the industrial automation sector (presence control of pieces, motion sensors, light intensity measurement) or at an individual’s household (roller shutters, car headlights, etc.)
How to choose a photoelectric sensor?
To choose a photoelectric sensor, you must have in mind 3 elements.
How close you want the object to be detected, the supply voltage, the reflectivity of the object to detect as well as the type of output contact (NO or NC).
The different types of detection:
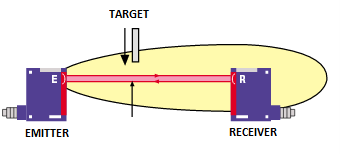
Through-beam:
There are 2 optical sensors. An emitter directs the beam, and a receiver collects the information. If the receiver does not receive the beam, it indicates that there is an object or an element.
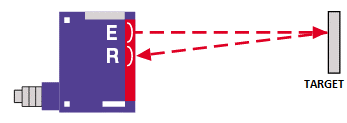
Diffuse:
The emitter/receiver are in the same box and produce a light beam. If an object passes in the beam, it will reflect on the object and it will be sent back to the emitter/receiver which will detect the object.
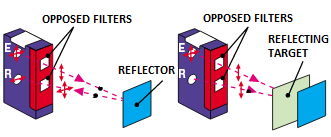
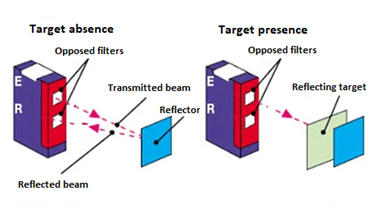
Reflecting:
There is an emitter/receiver that sends a beam to the reflector which then reflects it. When an object passes, the beam is not sent back. Thus, there is a detection.
Polarised retro:
It is similar to the reflecting solution, but it enables to detect non-opaque objects.