3.2.1 Electrical cables and wires
Complete range of industrial electrical cables for cabling
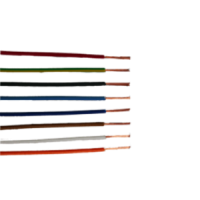
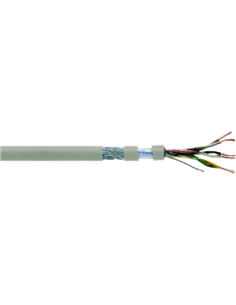
- Rigid or flexible multicore wires and cables shielded or unshielded, standard or for power, for data transmission or probes.
- Cables RO2V, HO7, HO5, VK.
- Cross-section from 0.75 mm² to 25 mm².
- All colours.
- Sold by metre or in coils: up to 500 m of cable.
Cable availability: 24 hours
Discover a wide range of wires and cables available at easi-spare.com: delivery within 24 hours and up to 500 metres of cable.
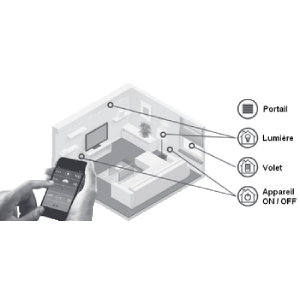
Electrical cables and wires are necessary to connect your electrical installations. Cables are sold on easi-spare.com by metre or coil for your connections. For specific requests, you can fill in a quote request. Our range of wires and cables with cross-sections from 0.75 mm² and 25 mm² can be used for any type of connection: house or industrial.
Electrical wire
An electrical wire consists of a conductive material, surrounded by an insulating sheath. Generally, the conductor is made of copper and the sheath is made of plastic.
There are various coloured wires, which correspond to the following inputs:
- Blue wire: neutral
- Yellow and green wire: earth
- Other colours (red, black, brown…): phase
Neutral and phase wires are insulated, earth wires can be insulated, or not.
There is an international codification created for choosing your wire. For example, EASI-Spare sells H05 and H07 wires: it corresponds to the rated voltage.
Electrical cable
The cable contains several electrical wires inside the same sheath.
To choose your electrical cable, here are the characteristics to consider:
- Rigidity: flexible cable, shielded…
- Cross-section: the thicker the cable, the more current it will carry
- Number of wires inside: the most common cable contains 3 wires: neutral, phase and earth.
- Insulation around the wires for protection: the sheath is usually in plastic or metal.
Make sure to choose your cross-section (in mm²) according to the power of your circuit. Example:
- 1.5 mm² cross-section for a current of 10 Amperes
- 2.5 mm² cross-section for a current of 16 to 20 Amperes
- 4 mm² cross-section for a current of 25 Amperes
- 6 mm² cross-section for a current of 32 Amperes